Studien & Publikationen.
Wir legen großen Wert auf wissenschaftliche Evidenz und standardisierte Methoden. Hier finden Sie die Ergebnisse unserer RCT-Studien und weiterer Forschungsarbeiten, die als Basis unserer wissenschaftlichen Arbeit dienen.
Publikationen bilden die Basis der wissenschaftlichen Evidenz bei Kranus Health.
A Randomized Trial of an App-Based Therapeutic for Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms
Christian Gratzke, Sandra Schönburg, Sven Eger, Katharina Raude, Markus Gabbert, Sophie Astheimer, Jan Halbich, Dirko Hercher, Waseem Mousa, Ralph Raschke, Bastian Keck, Oleg Krivov, Erik Krieger, Kurt Miller, Laura Wiemer
New England Journal of Medicine Evidence - 25.03.2025
Abstract: Male lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) increase with age and negatively impact quality of life. Conservative treatment with physiotherapeutic approaches and changes in lifestyle are often neglected. App-based therapeutics may have some benefits for patients with LUTS.
App-based Therapy of Erectile Dysfunction Using a Digital Health Application (EDDIG Study): A Randomized, Single-blind, Controlled Trial
Sabine Kliesch, Jann-Frederik Cremers, Claudia Krallmann, Robin Epplen
Bettina Scheffer, Tim Schubert, Maria Schubert, Nici Markus Dreger, Ralph Raschke, Ehsan Khaljani, Andreas Maxeiner, Kurt Miller, Laura Wiemer, Michael Zitzmann
European Urology Focus - 08.06.2024
Abstract: While international guidelines advocate for a multifaceted approach to treating erectile dysfunction (ED) involving physical activities, psychological support, and education, structured programs are infrequent. To address this gap, an app-based therapy was developed, offering a systematic approach. This randomized, single-blind controlled trial aimed to assess the effectiveness of an app-based therapeutic in improving ED.
Defining the Minimal Important Difference in International Prostate Symptom Score for Men with Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Using a Patient-centered Anchor Measure
Laura Wiemer, Walter Lehmacher, Sandra Schönburg, Christian Gratzke, Kurt Miller, C. Patrick Papp
European Urology Open Science - 09/2025
Abstract:This study aimed to determine the minimal important difference (MID) for the International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS) using data from a randomized controlled trial evaluating the app-based therapy Kranus Lutera for men with lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS). After 12 weeks of digital therapy, the MID—defined as the mean IPSS change among patients reporting “minimally improved” on the Patient Global Impression of Change—was 5.26 points (95% CI 4.38–6.13). Subgroup analysis showed a higher MID in men with severe baseline symptoms (8.23) compared to those with moderate symptoms (4.00). These results provide an important reference for interpreting clinical outcomes in LUTS treatment and for the design of future trials.
Differential impact of digital therapy on storage and voiding LUTS: A post-hoc IPSS analysis from the BEST randomized controlled trial
Sandra Schönburg, Christian Gratzke, Kurt Miller, Erik Krieger, Patrick Papp, Laura Wiemer
BJUI COMPASS - 25.09.2025
Abstract: This post-hoc analysis of the 12-week randomized controlled BEST trial (conducted between April and November 2023) investigated whether storage or voiding symptoms respond more favorably to the use of Kranus Lutera, the first app-based digital therapeutic for men with lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS). Participants using the digital therapy showed a significant and clinically relevant improvement in the total IPSS score compared to the control group (−7.0 points; 95% CI −8.1 to −5.9; p < 0.0001). Detailed item-level analysis revealed that improvements were consistently greater for storage than for voiding symptoms, with the largest effects observed in frequency, nocturia, and the feeling of incomplete bladder emptying. These findings suggest that structured app-based therapy may particularly benefit storage symptoms in men with LUTS and underline the value of Kranus Lutera as an effective component of standard care.
App-Based Therapy for Female Urinary Incontinence: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Prof Axel Haferkamp, M.D., Ph.D, Lisa Frey, M.D., Gregor Duwe, M.D., Jan Hendrik Börner, M.D., Carola Hunfeld, M.D., Prof Kerstin A. Brocker, M.D., Ph.D., Stella Troilo, M.D., Prof Walter Lehmacher, Ph.D., C. Patrick Papp, M.D., Prof Kurt Miller, M.D., Ph.D., Laura Wiemer, M.D.
The Lancet Digital Health - 12/2026
Abstract: This randomized, controlled, single-blind multicenter trial evaluated the efficacy of the app-based digital therapeutic Kranus Mictera in addition to standard care for women with stress, urge, or mixed urinary incontinence. A total of 194 participants received either Kranus Mictera plus standard care or standard care alone for 12 weeks. The intervention group showed a significant 61% reduction in daily incontinence episodes (between-group difference −59%; 95% CI: −71.7 to −46.7; p < 0.0001), with 92% reporting improvement and 23% achieving complete continence. Secondary outcomes also improved significantly, including symptom severity, quality of life, and patient activation. These findings demonstrate that Kranus Mictera effectively and safely complements standard therapy, providing a low-threshold digital treatment option for women with urinary incontinence.
Evaluating the impact of digital therapy for male LUTS: insights from the BEST trial subgroup analysis
Laura Wiemer, Christian Gratzke, Kurt Miller, Erik Krieger, Patrick Papp, Sandra Schönburg
World Journal of Urology - 01.11.2025
Abstract: Men with lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) represent a heterogeneous population, and this pre-specified subgroup analysis of the BEST trial evaluated the effectiveness of the digital health application Kranus Lutera. In this randomized controlled trial, 237 men received either app-based therapy plus standard care or standard care alone, with primary endpoints including 12-week changes in the International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS) and the Overactive Bladder Questionnaire Short Form (OAB-q SF), and additional outcomes assessing voiding frequency, urgency episodes, and adherence. Across all subgroups—stratified by diagnosis, symptom severity, age, and medication use—the intervention group demonstrated clinically meaningful improvements in IPSS (−6.4 to −7.4), with the largest effect in severe LUTS (−10.7, p < 0.0001), supported by improved OAB scores and reductions in daytime (−1.33), nighttime (−0.18), and urgency episodes (−1.59). Adherence was high, with 84% using the app multiple times per week, highlighting its broad applicability and benefit in routine clinical practice.
Evaluating the Impact of Digital Therapy for Male LUTS: Insights from the BEST Trial Subgroup Analysis
Laura Wiemer, M.D.
UroToday - 12/2026
Abstract: App-based therapy is no longer just a novel concept—it can meaningfully improve lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) in men. Subgroup analyses from the recent BEST trial show that Kranus Lutera, a structured 12-week digital therapeutic, provides clinically relevant improvements regardless of age, diagnosis, baseline symptom severity, or concurrent medication. Men with severe LUTS and urge-predominant symptoms experienced the largest benefits.
Key findings include consistent efficacy across BPH, OAB, and mixed presentations; additive benefits alongside medication; confirmed behavioral impact through reduced voiding and urgency episodes; and high patient adherence (84%). Digital therapeutics like Kranus Lutera bridge gaps in conservative LUTS management, delivering guideline-based exercises, bladder training, diaries, and education in an accessible, side-effect-free format that patients can use anytime, anywhere.
Digitale Gesundheitsanwendungen in der Urologie
Sandra Schönburg, Christian Gratzke, Kurt Miller, Laura Wiemer, Sabine Kliesch
Die Urologie 9/2024, Springer Medizin Verlag GmbH
Digitale Gesundheitsanwendungen (DiGA) wurden 2020 in die reguläre Versorgung aufgenommen und können auf Rezept verschrieben werden, wobei die Kosten von den Krankenkassen übernommen werden. In der Urologie gibt es aktuell zwei DiGA: Kranus Edera für erektile Dysfunktion (ED) und Kranus Lutera für benigne Prostatahyperplasie/überaktive Blase (BPH/OAB). Der Fokus liegt dabei auf rechtlichen Grundlagen, klinischen Ergebnissen und der praktischen Anwendung dieser DiGA.
Neuer Therapieansatz bei erektiler Dysfunktion: Leitliniengerechte Therapie mit DiGA
Abdol A. Ameri, Weidenstetten
Die Urologie 9/2024, Uro News 9/2024 Springer Medizin Verlag GmbH
Die digitale Gesundheitsanwendung (DiGA) Kranus Edera ermöglicht Patienten mit erektiler Dysfunktion (ED) organischer Ursache eine evidenzbasierte, leitliniengerechte und vollerstattungsfähige Therapie. Die App bietet eine ganzheitliche sowie ursachenorientierte Behandlung der ED. In einer prospektiven, randomisierten, kontrollierten Studie über 12 Wochen führte die Anwendung derTherapie zu signifikanten Verbesserungen der Erektionsfähigkeit, Lebensqualität und Patientensouveränität.
Klinische Expertise in jeder Therapie.
Kranus Health legt großen Wert auf exzellente wissenschaftliche Arbeit und zielt darauf ab, Patient:innen den Zugang zu qualitativer urologischer Versorgung zu vereinfachen. Unsere digitalen Therapieangebote sind das Resultat umfangreicher Forschung, entwickelt von einem interdisziplinären Team mit Mitgliedern aus Wissenschaft, Urologie sowie Physio- und Psychotherapie.
Durch unabhängige Studien werden unsere Therapien in RCTs validiert. Diese Forschungsarbeit wurde in Zusammenarbeit mit führenden Expert:innen durchgeführt:
Prof. Dr. med. Sabine Kliesch - Uniklinikum Münster
Prof. Dr. med. Christian Gratzke - Universitätsklinikum Freiburg
Prof. Dr. med. Sandra Schönburg - Universitätsklinikum Halle
Prof. Dr. med. Axel Haferkamp - Universitätsklinikum Mainz
Umfassende medizinische Integrität.
Wir legen besonderen Wert auf eine ganzheitliche und integrative Umsetzung der medizinischen Leitlinien. Unsere Therapien vereinen leitlinienkonforme physio- und psychotherapeutische Interventionen mit Lebensstilmodifikationen für eine umfassende Betreuung.
Dabei berücksichtigen wir die Qualität, Effizienz und Datensicherheit unserer Therapien, die durch BfArM- und CE-Zulassungen gewährleistet sind.
Klinische Wirksamkeit durch RCT-Studien validiert.
Die RCT-Studien bestätigen die Wirksamkeit von Kranus Edera und Kranus Lutera. In beiden Fällen zeigen sich statistisch signifikante Verbesserungen der relevanten Endpunkte.
Kranus Edera.
Digitale Therapie zur Behandlung erektiler Dysfunktion.
Studienleitung:
Prof. Dr. med. Sabine Kliesch (Uniklinik Münster)Kontrollierte Randomisierte Studie
241 Teilnehmer
hohe Therapieadhärenz bei 88,9% der Patienten
Primäre Endpunkte
Erektile Funktion (IIEF-5)
Lebensqualität (QoL-Med)
Patientenaktivierung (PAM-13)
Sekundäre Endpunkte
Blutdruck
BMI
Bauch- und Hüftumfang
Kranus Lutera.
Digitale Therapie zur Behandlung von Blasenentleerungsstörungen bei BPH und OAB.
Studienleitung:
Prof. Dr. med. Christian Gratzke (Uniklinik Freiburg), PD Dr. med. Sandra Schönburg (Uniklinik Halle)Kontrollierte Randomisierte Studie
237 Teilnehmer
hohe Therapieadhärenz bei 89,6% der Patienten
Primäre Endpunkte
International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS)
Sekundäre Endpunkte
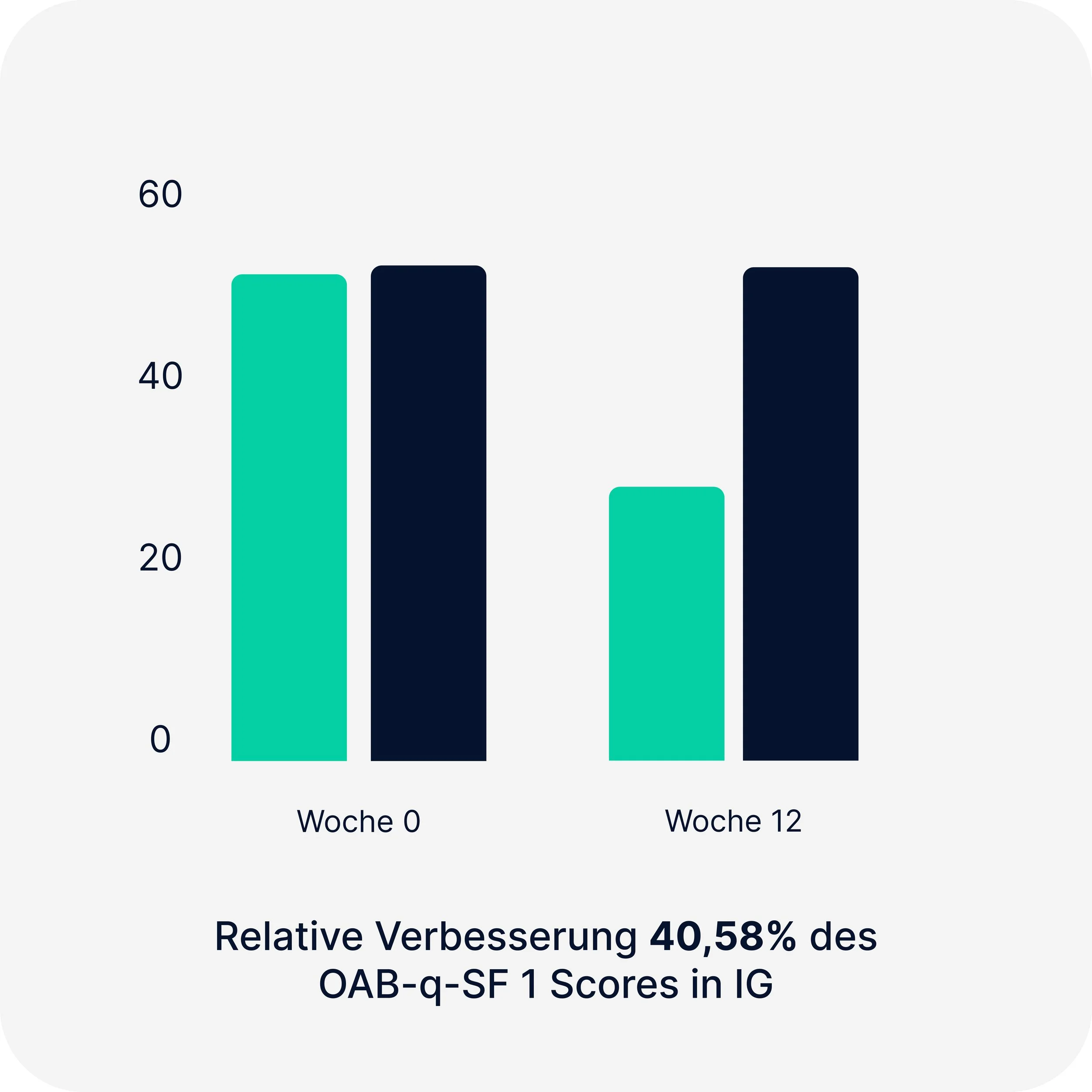
Overactive Bladder Questionnaire
(OAB-q SF 1)Overactive Bladder Questionnaire
(OAB-q SF 2)
Interventionsgruppe
Kontrollgruppe
* Analysen im FAS mittels J2R Imputation